An ES6 Module is just a file!
ES6 Modules can be used to create scope. All you need to do is to tell the browser to consider script.js as a "module".
<script type="module" src="script.js"></script>
Notice the use of
type="module"attribute in the<script>element.
Modules work only via HTTP(s), not in local files If you try to open a web-page locally, via
file://protocol, you'll find that scripts attributed as "module" are blocked by CORS policy. Use a local web-server such as VS Code Live Server Extension to test modules.
As it can be seen in the image below, you will not be able to access the number variable.
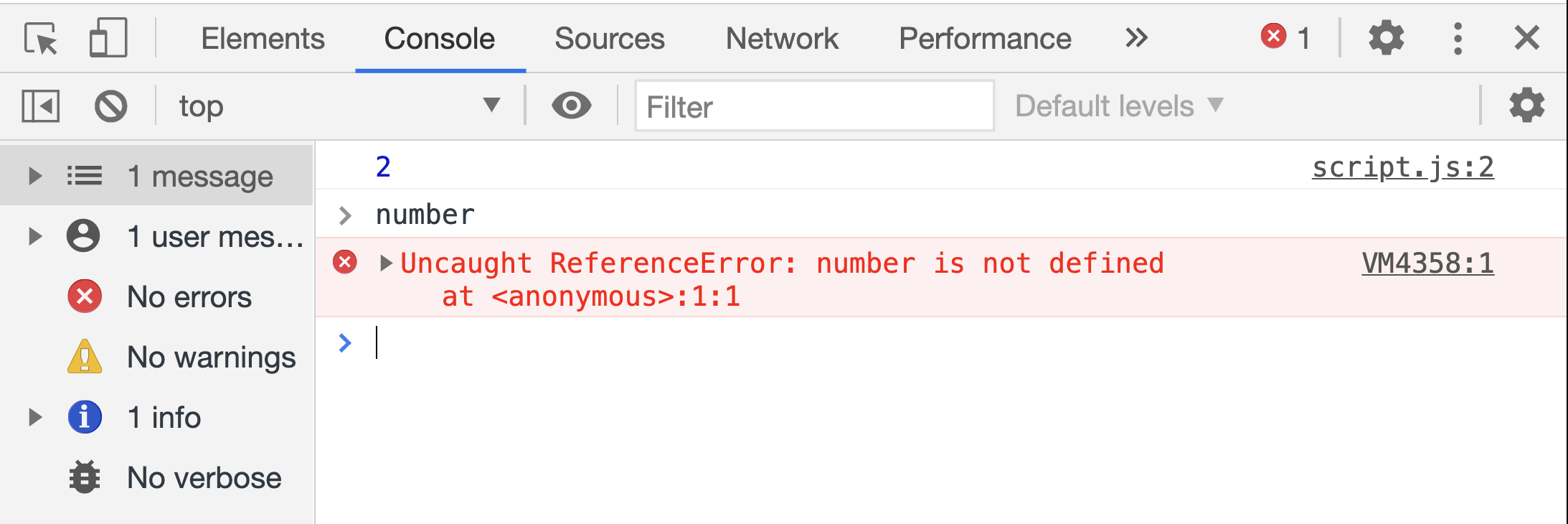
Notice the content of script.js is still simply the following two lines
// script.js file
const number = 2;
console.log(number);
With ES6 modules, each file has its own scope. To make values (objects, functions, classes, etc) available to the outside world, you must first export the value and then import the value where needed in other modules (files).