Step 9
Let me emphasize Git and GitHub are not the same! Git is a version control system, whereas GitHub is a repository hosting service and a collaboration platform. GitHub provides a lot of useful services for hosting software projects. We will explore some of these features in this course.
GitHub Pages
Let's start with a fun one! GitHub Pages allows you to host a website from your repository. By default, GitHub Pages uses a static site builder called Jekyll. We, however, already built our website. We don't need Jekyll! To let GitHub know that, we must add a .nojekyll file to our repository.
Go to your local repository (the sleeptime-git folder on your computer) and add the file .nojekyll. The file has a leading dot in its name and no content (it's empty).
Commit the changes:
git add .nojekyll
git commit -m "Add .nojekyll"
Although the changes are committed on your local repository, the remote repository on GitHub is behind your local repository.
To sync the local and the remote repositories, you need to push the latest local commits to the remote repository. You can do so simply by running the following command:
git push
Now go to GitHub, to your repository page. There must be a .nojekyll in there.
Next, open the "settings" tab in your GitHub repository. Find the section for "GitHub Pages" and set its source to the "master" branch as seen in the image below.
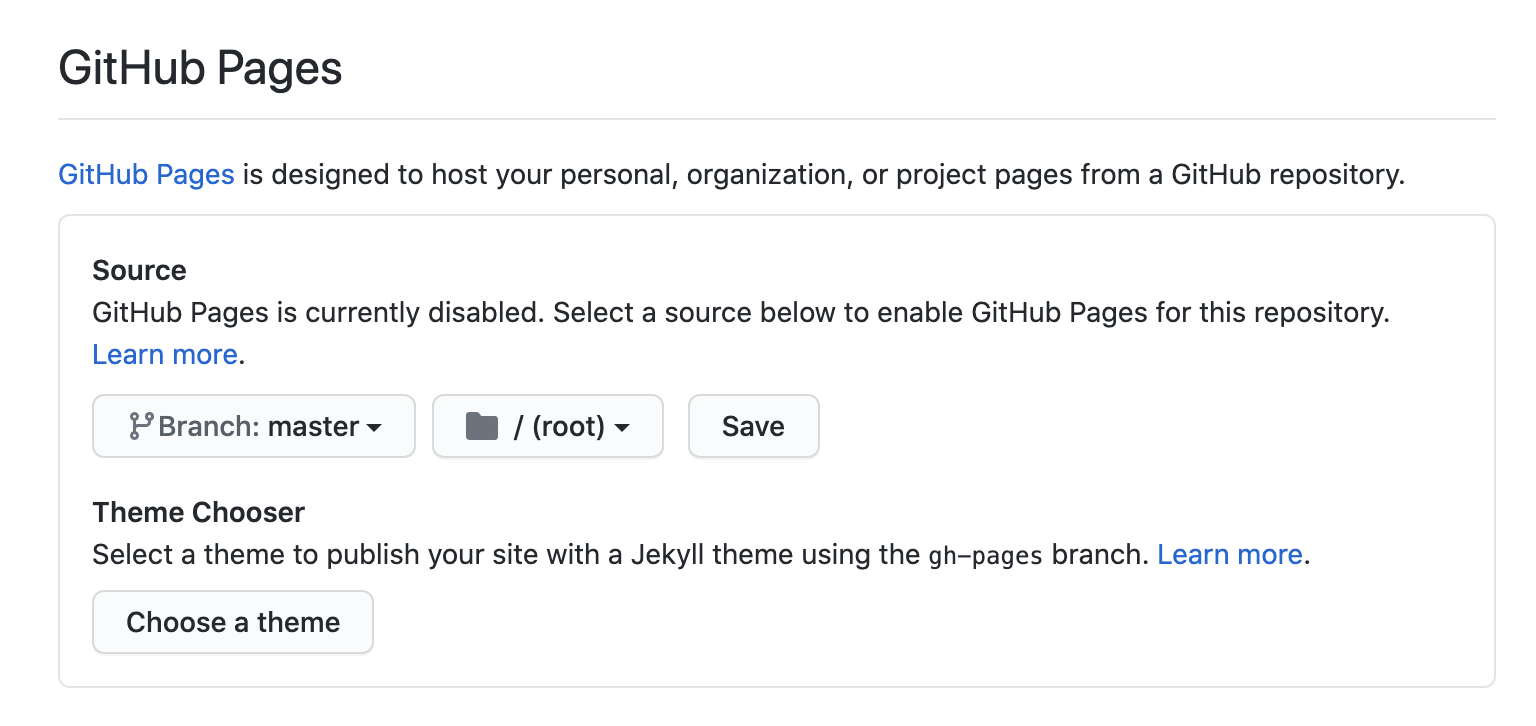
As soon as you save the changes, GitHub will show a message indicating "your site is published at ..."
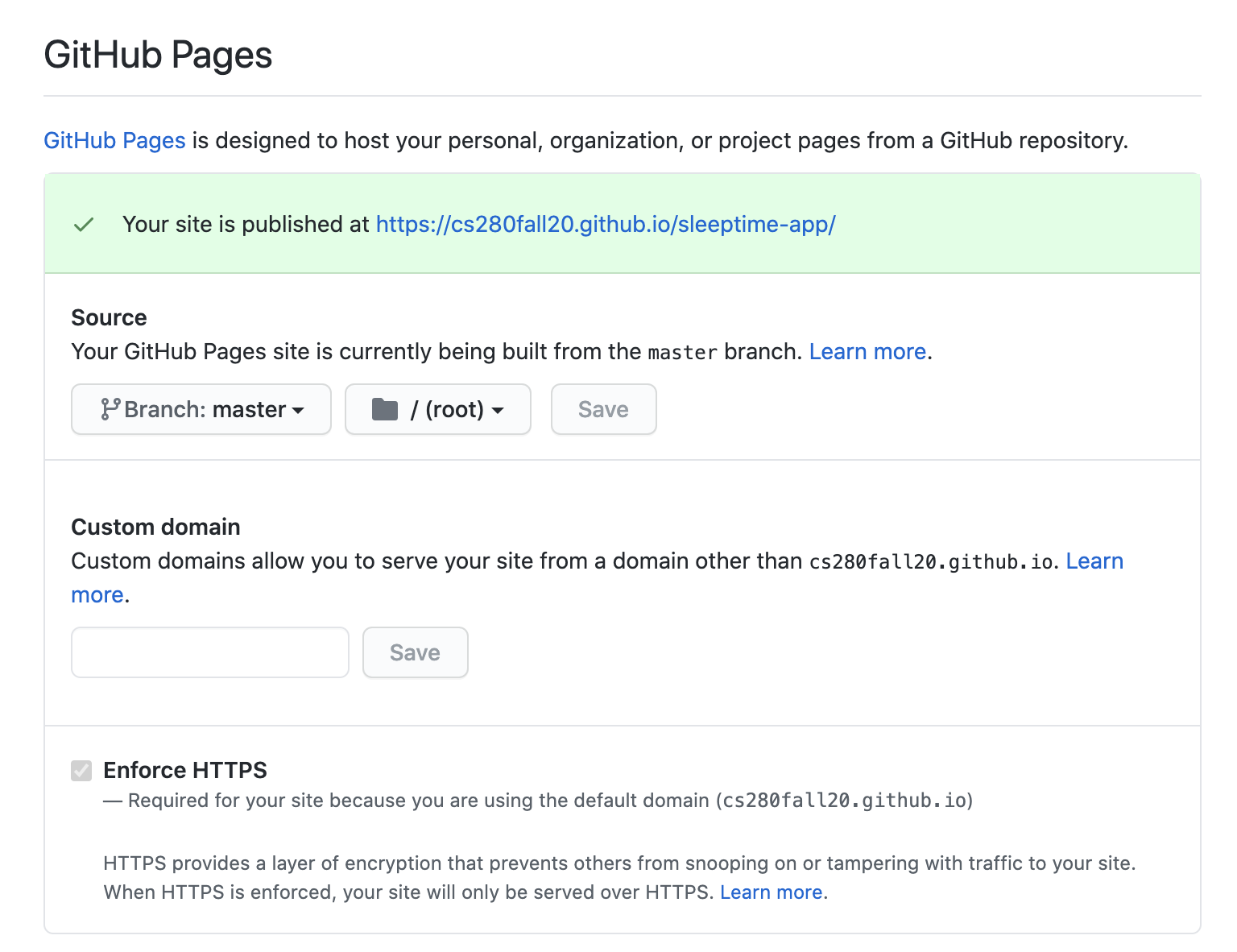
The GitHub Page I've created is available here. Go ahead and share yours with your friends!